What are the minimum requirements for windows xp. Windows XP operating system and computer technical requirements
This chapter explains all the requirements that you must meet before installing the Windows XP operating system. The minimum and recommended computer configurations are given, and the sequence of actions before Windows installation XP.
System Requirements
operating system Windows XP is more demanding on computer resources compared to previous versions. Therefore, if you have one of the previous versions of Windows installed, be sure to read this section before installing Windows XP, since your computer may not be powerful enough to work comfortably with this operating system. The minimum and recommended system requirements announced by Microsoft are presented in table. 2.1.
In fact, these requirements are underestimated, that is, you will be able to install the system, but the operating speed will be far from ideal. To achieve acceptable system speed, you will have to spend a lot of time configuring Windows XP. Therefore, in Table. 2.2 specifies the minimum and recommended requirements necessary for normal operation Windows XP without additional settings.
Table 2.2. Real System Requirements.

As you can see, the difference is quite significant, but it is the data from the table. 2.2 will allow you to achieve comfortable work in Windows XP without resorting to additional settings systems.
Preparing your computer for installing Windows XP
Let's prepare to install Windows XP. We will need a bootable CD with the Russian version of the Windows XP operating system, as well as a computer that meets the requirements given in table. 2.2.

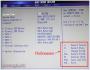
Rice. 2.1. Main BIOS window.
Before you begin the installation, you need to make a few changes to the BIOS.
1. Turn on your computer.
2. When the screen appears with a black background, press the Del key (sometimes the F2 key is used instead of the Del key).
3. A screen similar to the one shown in Fig. will appear. 2.1.
NOTE
The appearance of your BIOS may vary as there are two most common BIOS versions: Award BIOS and Phoenix BIOS (the latter is shown in Fig. 2.1).
4. Now using the keys<– и -> go to the Boot tab.
5. Using keys 8 and 2, select CD-Rom Drive and press the + key until CD-Rom Drive is the first item in the list (Fig. 2.2).

Rice. 2.2. Selecting a download source.
6. Press the F10 key.
7. In the window that appears, select Yes and press Enter (Fig. 2.3).
NOTE
If appearance your BIOS does not look like the one shown in Fig. 2.2 and 2.3, you have Award BIOS installed. In this case, in steps 4 and 5, use keys 8 and 2, select Bios Features, in step 1-st Boot device use the Page Up, Page Down keys to select the CDROM value.

Rice. 2.3. Saving changes.
You may have a question: “Why do we need all this?” This is done so that the boot occurs from the CD on which the distribution kit of the Windows XP operating system is located.
This completes the preparation for installing Windows XP. Insert the Windows XP operating system CD and proceed to Chapter 3.
Windows XP- the next version of the Microsoft operating system, after Windows 2000 and Windows Millennium, released on October 25, 2001. According to users, it is the most successful and stable OS in the Windows family.
Windows XP integrates Windows 2000 with Windows 98 and Windows Me. Windows XP was based on improved Windows 2000 code, and different versions for home computer users and business users. Unlike Windows 2000, which came in both server and client versions, Windows XP is a client-only system. Its server version is the later released Windows Server 2003.
As of June 30, 2008, Microsoft stopped supplying Windows XP to major PC manufacturers and retailers. The exception is small companies that will receive licenses for XP until the end of January 2009. The same applies to manufacturers of ultra-cheap PCs, who will be able to install the system until mid-2010.
The main support cycle for the OS ended in April 2009, since then there has been an extended support cycle that will last until April 2014. In 2010, Microsoft announced that the ability to downgrade from Windows 7 to Windows XP will remain until 2020. explaining this by the high popularity of the system. As of July 2010, this OS was used on 74% of corporate PCs worldwide.
Innovations
- Fast user switching feature. When switching, it is not necessary for the user who was previously working on the computer to log out of the system, saving the files that were open to them. Windows XP uses Terminal Services technologies to start each new user session as a separate Terminal Services session, with each user's data completely separate from each other. Each such session requires an additional approximately 2 MB RAM(excluding the amount of memory used by applications running in each session).
- New design style. Windows XP has new styles and themes that use 24-bit color icons and colors. The appearance of the Start menu has been changed. The top of the menu displays the user's five most frequently used programs, as well as the default email program and web browser.
- Search Companion Search Bar. Windows XP makes searching easier by grouping related search tasks into a dedicated search bar (Search Companion)
- Grouping files. Windows XP introduces new principles for organizing the taskbar, consisting of grouping several documents of the same application. For example, instead of placing multiple Microsoft Word documents on the taskbar, Windows XP groups the documents into a group that can be viewed by clicking a single button on the taskbar. Moreover, only this button with information about the quantity will be displayed on the taskbar open documents this application. When you click the button, a vertical list with the names of all documents is displayed.
- Support for new multimedia technologies.
- Windows Media Player 8. Windows XP uses the eighth version of Windows Media Player, which brings together key media operations, including playing CDs and DVDs, managing Media Player, creating media files and CDs, playing Internet radio, and recording multimedia files to portable devices.
- Windows Movie Maker. Windows Movie Maker version 1.1 supports basic capabilities for recording and creating files in the Windows Media format, as well as editing video and audio materials, saving and publishing Windows files Media. Although the utility you use only delivers content in Windows Media format, it can import files of any format and compression type supported by the DirectShow architecture.
- Digital photo support. Windows XP makes it easier to use digital devices and provides advanced capabilities for working with images, for example, publishing them on the Internet, sending photos via email(including in compressed form), including pictures in an automatic slide show and increasing the image display scale.
- Improved compatibility with apps and devices. Windows XP includes plug and play support for hundreds of devices that were not included in Windows 2000, as well as improved support for USB (Universal Serial Bus), IEEE 1394, PCI (Peripheral Component Interface), and many other bus standards and types. .
- Native CD and DVD support. Windows XP includes native support for reading and writing DVD-RAM optical discs and the ability to read UDF 2.01 (Universal Disk Format). In addition, using the IMAPI (Image Mastering API) interface, a Windows XP user can create CDs in write-once or write-once formats (CD-R or CD-RW) using the usual drag-and-drop method or appropriate wizards. When you save or copy a file to a CD, the operating system first creates it full image on the computer's hard drive and then transfers the data to the CD burner for final burning.
- Application Compatibility Mode. To use applications that were originally developed for previous versions of Windows and do not work in Windows environment XP, you can use Application Compatibility Mode. In this mode, the environment of previous versions of operating systems, starting with Windows 95, is emulated.
- Improved network services and communication services
- Universal Plug and Play support. The Universal Plug and Play standard allows devices to dynamically connect to a network, obtain an IP address, advertise their capabilities, and detect the presence and information of other devices on the network.
- Home Network Wizard. The Home Network Wizard automates network setup and Internet sharing. Its operation is carried out in bridge mode, which allows installation local network without requiring the user to have any knowledge regarding network protocols and physical features of the network being configured.
- Integrated Help and Support. Microsoft merged help desk and services technical support, so you can now access Remote Assistance, automatic updates, built-in Help and more from within single center Help and Support Center.
- Innovations that improve your mobile experience
- Power management. Like Windows 2000, power management in Windows XP is based on the ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) specification. Windows XP uses the ACPI specification, implemented in Windows 2000, to provide additional capabilities that the operating system uses to manage power to the computer and other equipment.
- Improvements for mobile users
- ClearType technology support. ClearType represents new technology display of text available in software products, with the help of which the horizontal resolution increases three times. This significantly improves the display of text on standard digital LCD monitors.
- Automatic configuration for multiple networks. This feature provides easy access to network devices and the Internet, allowing you to connect a laptop computer to both corporate and home networks.
- Remote desktop control. The Remote Desktop feature is based on Terminal Services technology. Thanks to this feature, the user can from any client running the operating system Microsoft Windows, run applications on remote computer, working under Windows control XP Professional.
- Improved reliability
- Driver rollback. When updating a driver, a copy of the previous driver package is automatically saved in a special subdirectory system files. If new driver will not work satisfactorily, the user can restore the previous version of the driver.
- System Restore. Functionality System Restore allows you to return your computer to the state it was in before the problem occurred. There is no loss personal files data, which may contain, for example, documents, images or email messages.
- Disaster recovery. The Automated System Recovery (ASR) feature allows you to save and restore applications. This function provides a Plug and Play mechanism that is used to archive relevant registry keys and restore this information to the registry
- Security improvements
- Firewall. In Windows XP, Internet security is ensured by a built-in feature called a firewall. The firewall is a dynamic packet filter. It provides protection for computers directly connected to the Internet or connected through a computer that is an Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) host. Internet Connection Sharing) on which the firewall is located. Enabling the firewall ensures that all connection attempts made from the Internet that were not requested by local users are blocked.
- Controlled network access. Windows XP has a built-in security feature that prevents intruders from gaining access by limiting the rights granted to a user trying to gain access to your computer over the network to a set of privileges account"Guest".
- Encrypted file system. Encrypting File System (EFS - Encrypting File System) is based on encryption with public key; it uses the CryptoAPI architecture found in the Windows XP operating system. For encryption, the EFS system uses the advanced DESX (Data Encryption Standard) algorithm or the 3DES (Triple-DES) algorithm. The encryption procedure can be performed from Windows Explorer.
Editions
- Windows XP Professional Edition- an operating system designed for business users, containing features such as remote access to the computer desktop, file encryption, central management of access rights and support for multiprocessor systems.
- Windows XP Home Edition- a system for home computer users. It is released as an inexpensive “stripped-down” version of Professional Editon, but is based on the same core and, using some tricks, allows you to upgrade to an almost full-fledged version of the Professional Edition.
- Windows XP Starter Edition- a system specially designed for novice users. Distributed only with new entry-level computers. Windows XP Starter Edition includes only the basic features of Windows XP.
- Windows XP 64-bit Edition- The 64-bit edition was created to take advantage of the capabilities of the Intel Itanium 64-bit (IA-64) processor. Windows XP 64-Bit Edition supports up to 16 gigabytes of RAM and up to 8 terabytes virtual memory. The system has not been developed since 2005, since HP stopped developing workstations with Itanium microprocessors.
- Windows XP Media Center Edition- an operating system built on Windows based XP Professional with a slightly reduced set of network capabilities and containing additional multimedia capabilities.
- Windows XP Professional x64 Edition- special 64-bit version designed for AMD64 Opteron and Athlon 64 processors from AMD and processors with EM64T technology from Intel
- Windows XP Embedded is a component version of Microsoft Windows XP Professional c additional features for embedding and tools that support the process of developing specialized operating system images.
- Windows Embedded for Point of Service- a specialized software platform aimed at retail chains and service enterprises. Based on Windows XP Embedded Service Pack 2 technologies, Windows Embedded for Point of Service allows retailers, hotels, and system integrators to simplify the installation, use and management of terminal systems.
- Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs- an operating system for outdated PCs, created on the basis of Microsoft Windows XP Embedded Service Pack 2.
Updates
Service Pack 1
The first service pack for Windows XP - Service Pack 1 (SP1) was released on September 9, 2002. Among the innovations that appeared in it it should be noted:
- USB 2.0 support
- Ability to select default programs for different operations
- The Encrypting File System (EFS) now supports AES encryption with a 256-bit key.
- Supports hard drives larger than 137 GB
Service Pack 2
The second service update package, Service Pack 2 (SP2), was released on August 6, 2004 and added the following functions and capabilities to the operating system:
- New component “Windows Security Center”, designed to monitor the security of your computer: viewing the state of the firewall (firewall), settings automatic update and antivirus.
- Updated Windows Firewall.
- Block pop-ups in your browser Internet Explorer.
- Improved Outlook Express, with a new Attachment Manager that isolates attachments when you open them. This prevents you from opening potentially dangerous attachments that could infect your system with a virus or other dangerous code.
- Improved wireless support
- New drivers and updates
- Improved autorun functions, etc.
Service Pack 3
Yours Microsoft solution changed after a massive epidemic of the ransomware ransomware WannaCry, which used the EternalBlue exploit to infect computers. This is one of the tools stolen from the cyber group Equation, which is believed to be affiliated with the US National Security Agency. Distribution of these tools - exploits, backdoors, etc. - the group was engaged The Shadow Brokers.
EternalBlue was published by The Shadow Brokers in mid-April 2017. A few days earlier, Microsoft released a number of emergency patches for its developments. As it turned out after the release from Shadow Brokers, these patches closed multiple vulnerabilities used by Equation hackers. Apparently, someone warned Microsoft in advance.
At the same time, Microsoft management refused to release updates for the Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 operating systems, citing the fact that they had long been removed from technical support.
The new patches fix vulnerabilities attacked by exploits codenamed ENGLISHMANDENTIST (for the Outlook vulnerability), ESTEEMAUDIT (IIS 6.0) and EXPLODINGCAN (RDP).
Windows XP ranks fourth in the world in terms of prevalence: the share of the operating system is 5.66%. In China, some countries in Asia and Africa, Windows XP is still very widespread. Also, hundreds of thousands of ATMs around the world still operate specialized versions of this operating system. Support for two of them - Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 and Standard 2009 - will continue until 2019.
After graduation Windows support XP, Microsoft was forced to release an emergency patch for newly discovered vulnerabilities in the Internet Explorer browser (versions 6-11) on all versions of Windows, including XP.
Patches for Windows XP and Windows Server Microsoft initially did not intend to release 2003 against vulnerabilities exploited by Equation/NSA, citing the fact that these systems were no longer supported and that users should have switched to newer ones long ago software products. However, shortly after the WannaCry outbreak, Microsoft changed its mind, citing the overall state of the “threat landscape.”
| In reviewing this month's updates, we have identified a number of vulnerabilities that are highly likely to be subject to cyberattacks from government agencies... or their imitators,” Microsoft said in a statement. – To mitigate the threat, we are publishing additional security updates beyond what is released as part of our regular Update Tuesday program. These updates will be available to all users, including those using older Windows versions. Due to the increased threat of destructive cyber attacks, we have decided to take this step as these updates will provide additional protection against possible attacks similar in characteristics to WannaCry |
Microsoft calls this move “rare” and urges people not to view it as a deviation from their technical support standards. Experts are inclined to believe that such “rare steps” will be repeated from time to time.
| IN in this case the situation could hardly have been resolved any other way, says Ksenia Shilak, sales director at Sec-Consult. - On the one hand, Windows XP is outdated in all respects, on the other hand, millions of users continue to use it, sometimes forcedly. Choosing whether to leave these users unprotected in the face of a possible new cyber epidemic or give up some business principles, Microsoft settled on the second option. This is a rather risky step, but from an ethical point of view it seems more correct. |
System Requirements
Minimum hardware requirements to install Windows XP:
- 233 MHz Pentium processor or faster (at least 300 MHz recommended)
- At least 64 MB RAM (at least 128 MB recommended)
- At least 1.5 GB of free hard drive space
- CD or DVD drive
- Keyboard, Microsoft Mouse, or compatible pointing device
- Video card and monitor that support Super VGA mode with a resolution of at least 800x600 pixels
- Sound card, speakers or headphones (optional)
Problems
Installing the third service pack (SP3) for Windows XP has more than once led to problems with the PC. This is how the press described cases of endless rebooting of some PCs after installing SP3. At the same time it became inaccessible safe mode, which provides the ability to roll back the operating system to a previous state. On forums dedicated to this topic, users noted that after installing the third update package, their system rebooted, but could not begin to start Windows, each time sending the computer to reboot again.
Former Microsoft product security director Jesper Johansson analyzed messages on forums and came to the conclusion that this problem arose for two reasons independent of each other. The first thing Johansson noted was that in many cases the problem occurred on computers manufactured by Hewlett-Packard (HP). According to the specialist, this could be due to the fact that HP, and possibly other computer manufacturers, used the same image for computers with Intel and AMD processors during the factory installation of the operating system. As a result, the intelppm.sys driver was responsible for power management on all PCs, although systems with AMD processors have their own amdk8.sys driver. According to Johansson, running the intelppm.sys driver on a computer with AMD processor under normal conditions it did not lead to a failure, but with the installation of the third update package this led to the inability to load the operating system, or to reboot itself immediately upon startup. Another reason, according to the specialist, was related to the BIOS motherboard Asus A8N32-SLI Deluxe and probably other boards with AMD processors.
The problem was solved by disabling the intelppm.sys driver or connecting a USB flash drive or any other secondary storage device to the computer.
In addition, some users complained that after installing Service Pack 3, a large number of corrupted entries appeared in the registry of their system, and from the folder network connections disappeared network cards. Other users have reported the same issues occurring after updating on computers running Norton products. Symantec senior product director Dave Cole acknowledged that a number of users of the Norton series have experienced problems, but the number is small. According to him, Symantec tested its products with Windows XP SP3, but found no errors. Cole blamed Microsoft for all the troubles, saying that this was due to the XP SP3 package, which was already causing problems for users of some computers.
Microsoft responded to this situation with the following: “Customers having installation problems should contact Microsoft Support, who can provide free help and tips for troubleshooting problems."
After some time, Symantec nevertheless took on part of the responsibility and released a special free utility SymRegFix, which allows you to clean the registry from damaged entries. In addition, Symantec recommended that users of Norton programs who have not yet installed the third service pack for Windows XP disable the SymProtect feature before upgrading the OS to eliminate the risk of damaging the registry.
Windows XP News
Appearance of Vladimir Putin on the computer
In mid-December 2019, it became known that Russian President Vladimir Putin uses the outdated Microsoft Windows XP operating system both on the computer in his office in the Kremlin and in his official residence Novo-Ogarevo near Moscow. The president was betrayed by photographs published by his press service.

In a photo from a November press release, Putin sits at a computer in his Moscow residence, with an image of the Kremlin towers on his desktop. The bright blue taskbar at the bottom of the screen indicates that the computer is running Windows XP.
Windows XP support
Windows XP Service Pack 2 will continue to be supported until 2020
After the announcement of the end of official support for Windows XP Service Pack 2, it was reported that users of some editions of Windows 7 will continue to be able to use Windows XP for another 10 years. Such a solution is quite rare for Microsoft.
So far, it has been reported that Microsoft plans to set the deadline for returning to Windows XP to be six months from the date Windows startup 7. A little later, Microsoft extended the period to one and a half years, and the number “x” for Windows XP was assigned to the date of publication of the first package Windows fixes 7 SP1.
Microsoft can't ignore that Windows XP is still popular. Microsoft executives admit that 74% of corporate computers are still running Windows XP. And now the company's managers have announced a change in their plans. According to them, owners of Windows 7 Professional and Ultimate will have the opportunity to return to Windows XP Professional as long as the “seven” lives, and it has been given until January 2020. Windows XP Ultimate Edition will run until January 2015.
It is worth noting that this solution only applies to OEM copies of Windows 7 installed by PC manufacturers on new machines. "Organizations and individuals purchasing new computers will be able to take advantage of the right to return to Windows XP and Vista until they decide to switch to Windows 7," Microsoft manager Brandon LeBlanc said on the company's official blog.
As for other deadlines, installed by Microsoft in relation to Windows, they will remain in force. Equipment manufacturers will complete installation of Windows XP Home on netbooks by the end of 2010. And in a year, the supply of computers with Vista installed will stop.
Microsoft will be forced to continue supporting Windows XP for a long time to come
2014: Technical support for Windows XP and Office 2003 ended
On April 8, 2014, Microsoft announced the end of technical support for the operating system. Windows XP and a suite of office applications Office 2003.
Effective April 8, 2014, devices running Windows XP will no longer have access to security updates, automatic non-security patches, paid or free services support, updating technical documentation on the Internet. The timing of the end of support for Windows XP is consistent with Microsoft's product support policy, announced by the company in 2002.
Telecom Daily research confirms companies' interest in switching to new OS versions. The information and analytical agency surveyed representatives of more than three thousand companies in all federal districts of the Russian Federation. It has been established that Russian companies and organizations continue to actively use Windows XP. About 42% of working computers run this OS. Among the companies surveyed as part of the study, the Windows OS family accounts for more than 95% of the market in the “companies and organizations” segment.
The study also found that almost 63% Windows users XP is aware of the end of its technical support. At the same time, on modern licensed OS Windows family this year more than 40% of respondents plan to switch and another 28% plan to do this over the next 2-3 years. It also turned out that the main problem of switching to the current Windows OS is the fear of incompatibility of programs and applications, as well as a lack of funds.
“Windows XP was released more than 12 years ago, so today it lags behind new versions of the OS by as many as three generations and can no longer fully protect your data from security threats. Moreover, over the years modern technologies have stepped far forward: they have learned to store data in the cloud, leaving floppy disks and disks in the past. Concepts such as BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) and . It is obvious that when creating Windows XP could not take all this into account, so today the old OS does not allow you to follow current IT trends. It may not be compatible with many modern equipment and applications, said Sergei Martsynkyan, Windows promotion manager at Microsoft in Russia. “To meet the new needs and expectations of our customers, we create modern technologies and products.”
“The confrontation between those who attack and those who protect operating systems does not stop for a second. We must not forget that since 2001, when Windows XP appeared, cyber fraud has transformed from the indulgence of a few advanced amateur hackers into a multi-billion dollar international business. Attackers make huge profits by exploiting unprotected PCs. Without updating your OS and applications, and without thinking about using pirated versions Software, enterprises and private users risk becoming victims of cyber criminals, putting their own and corporate data, financial resources and reputation at risk,” emphasized Andrey Beshkov, manager of information security programs in the CIS countries at Microsoft in Russia.
Using an outdated operating system can also become an obstacle when connecting new or updating existing equipment. Windows XP does not support a number of features that are highly demanded by users and are available in modern operating systems. For example, at the time of the release of Windows XP, features such as support for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, high-resolution monitors and touch screens were not widespread.
“According to our estimates, there are fewer and fewer companies using Windows XP as a corporate standard. The transition to new versions of operating systems guarantees organizations regular receipt of security system updates, reduction in costs for supporting IT infrastructure, and working with modern applications and equipment, noted Denis Kuskov, general manager information and analytical agency Telecom Daily. “This is also supported by Microsoft's approach to working with customers, the company always keeps its customers in mind: it is an industry leader with a unique and compelling vision for the security, privacy and reliability of your data.”
Everything written in this article will be useful for those who do not believe in the stability of Microsoft. It’s worth saying right away that after reading it and trying the new Windows XP operating system, your opinion will most likely change dramatically. The tale that company operating systems are unstable is not only common among professional system administrators, but also between ordinary users. This opinion is not based on empty space; many remember Windows 95, the operation of which was associated with a large number of problems. In other words, quite serious hopes were placed on the system, but practically none of them came true.
Some time has passed, certain additions and corrections have been made to improve the work. An example of the effective work of Microsoft employees was Windows system 98, which differed very favorably from its predecessors. At this stage, the development of the system did not stop; quite a lot of systems were created, each of which became a certain prerequisite for the release of Windows XP.

In all respects, this is a new generation system, new compatibility and a completely new design. Those who heard certain information about the system and switched to it were satisfied and the number of such users is gradually increasing.
Windows XP from Microsoft
The new system is characterized by such properties and qualities as:
- new front-end design controls that make some common tasks easier and more efficient;
- it became possible to work with digital images, obtain high quality photographs and exchange them;
- there is a multifunctional tool designed to work with various musical materials that are able to search, store, play and download music files of the highest quality;
- there are all the necessary tools to create and view various videos on a PC;
- availability of ease of sharing access to a PC, as well as for creating a home network;
- there are means to solve some problems, as well as the opportunity to receive help from specialists;
- effective means of communication for transmitting various instant messages;
- the system is secure and stable, which ensures efficient and stable operation;
- security lies in the ability to encrypt files, which is important when storing corporate information;
- support provided mobile devices to be able to work autonomously or connect remotely;
- There is multilingual support, which makes it possible to effectively interact with users from all over the world.
As you can see, there are quite a lot of advantages, all of which contributes to the rapid growth of popularity of this system in the information world.
System requirements for Windows XP
In order to install Windows XP on a PC, it is necessary that the device complies with certain rules and regulations. These are certain system requirements that are quite stringent. First of all, it is worth noting that the system is not as demanding on the processor as it is on memory personal computer. This circumstance is evidenced by the result with which the processor is overclocked.
Now, regarding the requirements themselves. Microsoft Corporation officially states that for Windows XP to work effectively, you must have hardware whose characteristics will meet the following minimum system requirements:
- a computer with a processor with a clock frequency of at least 300 MHz; there is a certain acceptable minimum - 233 MHz (system with one or two processors), and processors of the Intel Pentium/Celeron, AMD K6/Athlon/Duron families or other, but necessarily compatible, processors can also be used;
- At least 128 MB of RAM is recommended, there may also be some acceptable minimum of 64 MB, but it is important to know that the performance and some capabilities of the operating system may be limited;
- At least 1.5 GB of free disk space is required;
- video card and Super VGA monitor, the resolution of which must be at least 800 by 600 pixels;
- DVD drive;
- Microsoft Mouse keyboard and mouse, but other compatible input devices will also work.
All of the above minimum system requirements for Windows XP may vary depending on the system configuration, some installed applications and the functions present. For example, if you are installing over a network, you may need additional free space on disk. There is still some equipment that is required to work efficiently and effectively with Windows XP. This sound card, modem, DVD drive, which is currently supported in hardware.
Important points
Microsoft Corporation, simultaneously with the development of the Windows XP system, with the fact that certain system requirements were established, declared a real war on pirates, and in a rather unique way. The essence of this process is that a specific key is generated for each personal computer, with its features and configurations carefully taken into account. In progress Windows activation XP the user sends the received key along with the key that was on installation disk to the corporation, which after some time registers a new user. Only after this can you begin installation.
The installation process of Windows XP, if the system requirements are fully met, is simple. At the very beginning, the PC is scanned for the presence or absence necessary drivers. Such moments as a reboot will be performed, some questions will be asked, after which the system will never bother its user with these questions.
If the system requirements are fully met, you can immediately be convinced that the operating system is able to amaze with its speed. As a rule, it takes approximately 7 seconds from the first press to full loading.
Conclusion
What attracts many people to the system is not its affordable installation requirements, but somewhat attractive design. Immediately after installing the system, the desktop looks perfectly clean. The harmony of colors and various shapes is at the highest level.

It is worth noting that there are some innovations, but they all become familiar after a few days regular work with the system. System compatibility is at an ideal level, everything required applications install and operate without any problems or complications, if, of course, all system installation requirements are met.
Professional? Here we will cover upgrading from an earlier version of Windows and how to implement this step.
System Requirements
If you don't use enough powerful computer, then when installing Windows XP Professional you will experience nothing but irritation. In this section, we'll look at the minimum system requirements for Windows XP Professional (and also touch on the 64-bit version of Windows XP Professional) and talk about some system compatibility testing tools.
Windows XP Professional
With each new version Windows minimum system requirements continue to rise. Don't be surprised that Windows XP Professional won't work on an old 25 MHz machine with 2 MB of RAM. To get Windows XP Professional to work, your computer must meet the following requirements.
- Processor 300 MHz or higher (recommended), 233 MHz minimum. Intel Pentium/Celeron family or AMD K6/Athlon/Duron family or compatible processors.
- 128 MB RAM or higher (64 MB minimum supported, but may limit some features).
- 1.5 GB free space on your hard drive.
- SuperVGA (800 x 600) or higher resolution of the video adapter and monitor.
- CD-ROM or DVD drive.
- Keyboard and mouse or other compatible pointing device.
These are the minimum system requirements for installing Windows XP Professional. If you want to work faster and more efficiently, then you should increase the power of any, and maybe all of the above components.
Windows XP Professional 64-bit edition
Although we are not going to discuss Windows XP Professional 64-bit edition in detail in this course, you may find that it is a better fit for your organization. Let's take a look at what the 64-bit version offers and what its requirements are.
Windows XP Professional and Windows XP Professional 64-Bit Edition differ from each other both in design and in their capabilities. Therefore, there are differences in installation requirements, disk space, and device drivers. This also applies to the installation and operation of certain applications such as Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
System Requirements. Table 2.2 shows the differences between Windows XP Professional and Windows XP Professional 64-Bit Edition.
Device drivers. Since Windows XP Professional 64-Bit Edition runs in a 64-bit environment, it requires 64-bit drivers. Some drivers allow installation of both 32-bit and 64-bit drivers from the same .inf file. The .ia64 extension is used within the .inf file of these drivers to indicate installation files installed on a 64-bit system. Earlier versions of Windows may not recognize the .ia64 extension.
| Component | Windows XP Professional | Windows XP Professional 64-Bit Edition |
|---|---|---|
| Processor (minimum) | 233 MHz | 733 MHz |
| Processor (recommended) | 300 MHz | Unlimited |
| RAM (minimum) | 64 MB | 1 GB |
| RAM (recommended) | 128 MB | Unlimited |
| Hard disk space | 1.5 GB | 1.5 GB |
Note. Don't pay attention to what is written about the device's software packages. Even if a software package says that it is compatible with Windows XP Professional, this does not mean that the device is compatible with Windows XP Professional 64-Bit Edition.
MMC. Since Windows 2000, Microsoft has included the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) in its operating systems. This is central control application, to which integrated applications are connected, allowing you to create a user control system. Using integrated applications allows administrators to track and work with multiple data from one place without missing any extraneous information. MMC can be used to work with group policy and network settings. In addition, the use of integrated applications allows programmers from other companies to develop their own applications. Figure 2.10 shows the MMC window.
Windows XP Professional 64-Bit Edition includes both 64- and 32-bit versions of MMC. By default, the 64-bit version is activated, although if necessary, you can select the 32-bit version. MMC versions cannot exchange integrated applications. Windows XP Professional recognizes the number of integrated applications available on the system and activates the version based on analysis of the integrated application algorithm.
Dual boot
If you already have Windows NT, Windows 2000 or Windows 98 installed, then you have the option of upgrading the current system or installing Windows XP Professional in parallel. For example, if you decide to install a new copy along with NT, you will have two systems to boot your computer from. This is called dual booting.
Rice. 2.10.
If you decide to have DOS or Windows 9X as an alternative operating system on your system dual boot, then part disk space should be formatted as FAT. For better results and fewer errors, this OS should be installed before installing Windows XP Professional. It is highly recommended that you host Windows XP Professional in your own section disk. Although the OS is in its own directory, if you install several copies of Windows in the same partition of disk space, they will write to the same directory Program Files. XP may overwrite some files there or change the access permission of some important files, making it impossible to boot the alternative operating system. Next, if you chose NTFS as XP file system, then it seems impossible to store NTFS files on a drive formatted as FAT.
Compatibility
To ensure the compatibility of computer hardware and programs with the Windows XP Professional operating system, Microsoft has created a product compatibility check page on its website (http://www.microsoft.com/windowsxp/pro/howtobuy/upgrading/compat.asp). Since the page is quite extensive, Microsoft has simplified the compatibility check process. Users can enter their computer model or software versions and the site does the rest. Figure 2.11 shows what this page looks like.
Technological progress does not stand still. Humanity strives for increased productivity. Operating systems are no exception: technological progress has affected them too. In this article we will look at the Windows XP and Windows 7 operating systems, compare their main indicators and identify the best one.
A little history
Before moving on to the “dissection” of operating systems, let’s tell them a brief history.
Windows XP
One of the most successful (after Windows 98) operating systems from Microsoft.
Windows XP is one of Microsoft's most successful operating systems
The target audience of the branded product is home and business users of various computer devices. This is the corporation's second attempt to abandon digital names for its products.
Windows XP went on sale on October 25, 2001 and was continuation of Windows 2000 Professional. Its name “XP” implies the English word “experience”, which means “experience”.
At the time of its commercial launch in 2001, it was considered one of the fastest operating systems. The Windows NT architecture has made it possible to reduce user costs when migrating from older versions due to support for familiar functionality and the ability to run legacy applications.
Support for Windows XP ended on April 8, 2014. However, Microsoft continues to release antivirus protection updates, since there are still users working with this operating system.
Also, the advantages of the new product are stable operation and the elimination of bugs with libraries that made previous versions of windows famous. On at the moment it is in a state of discontinuation of support by the manufacturer, yielding Windows place 7.
Windows 7
This operating system has overtaken Windows XP in popularity.
 Windows 7 is the most popular OS in the world
Windows 7 is the most popular OS in the world It entered the market in 2009. Potential consumers were treated to a number of significant innovations, support for high resolution and new television formats. The developers also fixed bugs in Vista and Longhorn OS, due to which these systems were not successful.
Windows 7 was released on October 22, 2009. As of 2017, it is the most popular operating system in the world.
Despite the introduction of new systems, Windows 7 remains beloved working environment many users. At the moment, its support continues.
Features and capabilities
Windows XP and Windows 7 have a number of differences.
Table: comparison of features and capabilities of Windows XP and Windows 7
| Parameter | Windows XP | Windows 7 |
| Search |
|
|
| Program launch control |
| Programs are launched by intelligent search: just enter the first letters of the name and press enter or click on the desired program. |
| Using multimedia |
|
|
| Support for home and office networks | Only an advanced user with certain skills can create a home network. |
|
| Child safety | It is not possible to create a safe environment for a child due to the difficulty of setting it up. | Security module allows parents to set zones hard drive and programs that are available to the child, as well as the length of time the child spends at the computer for each day of the week. |
| Sort files and folders | Finding files is difficult and requires memorizing locations. | A “Library” menu has appeared in Explorer, displaying all the locations of important documents, favorite music and family multimedia archive on all drives and devices. |
| Bug fixes | The help system does not provide a direct answer to asked question. Troubleshooting equipment problems can only be done by calling a specialist or at random. | Its own diagnostic system will detect the problem and suggest the best methods for solving it yourself. |
| Internet travel | At the time of writing, browsers for XP are no longer supported. Some operations required third party applications or several tabs. | Wide range of browsers to choose from. The functions of translation, information search, and file viewing are implemented in the form of browser plugins. |
| Using the desktop | The background gets boring after a week. The desktop was a home exclusively for icons without the ability to mount widgets. | The interactive desktop supports the installation of the necessary icons and notifications. The wallpaper has become animated. |