Apple hardware test does not start. Mac Diagnostics
The easiest way to avoid the help of service centers when searching for hardware problems (not all of them can boast of a good reputation) is to use the built-in Mac diagnostic methods. In this material we will tell you how to launch and use " " And " Apple Diagnostics».
Using standard diagnostic tools, you can effectively detect hardware faults (problems with hard drive, solid state drive, RAM, GPU, motherboard and other nooks and crannies of hardware). How to do this?
On which Macs which utility?
Regardless of (MacBook, iMac, Mac mini or Mac Pro) and the year of its release, the operating system includes a utility for self-diagnosis of the hardware. On computers manufactured before June 2013, it is called “ Functional test of Apple hardware"(Apple Hardware Test - AHT), and after - " Apple Diagnostics».
Before running any of the utilities, be sure to disconnect all peripheral devices (including optical drives, if such antiquity still exists) except for the keyboard, mouse, display and Ethernet adapter. Some versions of OS X Lion and later may require Ethernet or Wi-Fi to run the Internet version of AHT. It is no different from its offline counterpart.
To use AHT, be sure to connect your MacBook to a power source.
List of keyboard shortcuts
If you don’t have a mouse, the following shortcuts will come in handy:
- Option (⌥) + D: run diagnostics via the Internet;
- Command (⌘) + G: start operation;
- Command (⌘) + L: display a list of languages;
- Command (⌘) + R: run the test again;
- S: shutdown;
How to Run Diagnostics on Mac (Apple Hardware Functional Test or Apple Diagnostics)
Note: " Functional test of Apple hardware" And " Apple Diagnostics" work in the same way. The only caveat is for launching " Apple Diagnostics“An active Internet connection is required, and the interface will be much nicer.
1 . Turn on or restart your Mac if it's turned on.
2 . While turning on, press and hold the " D» until the language selection screen appears.
3 . Select a language (if a mouse is not connected to the computer, then select a language using the arrows and enter with the “Enter” key).

4 . Mac diagnostics will begin.

After the test is completed, the results will be displayed.

To exit the ANT utility, click the " Reboot" or " Turn off"at the bottom of the window.
What do the results say?
If problems with the hardware are detected during the test, then get ready to see an error and some explanatory details.
You can decipher AHT errors on the Apple technical forum, and in general I recommend that you go there first when looking for solutions to problems with Apple gadgets. True, you will need knowledge of English, at least with a dictionary.
Codes Apple errors Diagnostics and their decoding can be found below:
ADP000- No problems were found on the computer;
CNW001, CNW003, CNW004, CNW005, CNW006- There are problems with the Wi-Fi module on the computer;
CNW007, CNW008- Not detected Wi-Fi networks. Available networks There is no Wi-Fi, or the Wi-Fi module is faulty;
NDC001, NDC003, NDC004, NDC005, NDC006- The camera is faulty;
NDD001- There is a problem with the USB module. Disable everything external devices, except for the keyboard, mouse and Ethernet adapter. Run the scan again. If this code appears again, contact your service center;
NDK001, NDK003, NDK004- There is a problem with the keyboard;
NDL001- There is a problem with the Bluetooth module;
NDR001, NDR003, NDR004- There is a problem with the trackpad;
NDT001, NDT002, NDT003, NDT004, NDT005, NDT006- There may be a problem with the Thunderbolt module. Disconnect external Thunderbolt devices and run the scan again. If this code appears a second time, contact your service center;
NNN001- Failed to detect serial number. The computer requires service, contact service;
PFM001, PFM002, PFM003, PFM004, PFM005, PFM006, PFM007- There is a problem with the system management controller (SMC);
PFR001- There may be a problem with the computer firmware;
PPF001, PPF003, PPF004- There may be a problem with the fan;
PPM001- There is probably a problem with the memory module;
PPM002, PPM003, PPM004, PPM005, PPM006, PPM007, PPM008, PPM009, PPM010, PPM011, PPM012, PPM013, PPM014, PPM015- There may be a problem with the built-in memory;
PPP001, PPP002, PPP003- There is probably a problem with the MagSafe power adapter. Try unplugging the power adapter from your Mac and the outlet, then plugging it in again. Run the scan again. If this code appears a second time, contact your service center;
PPP007- There may be a problem with the power adapter or it is not connected. To test the power adapter, reconnect it to your computer and wall outlet. Run the scan again. If this code appears a second time, contact your service center;
PPR001- There is probably a problem with the processor;
PPT001- The battery could not be detected;
PPT002, PPT003- The battery will need to be replaced soon. It is operational, but its capacity has decreased.
PPT004, PPT006- The battery requires maintenance. The battery is faulty, although this may not affect its performance or capacity;
PPT005- The battery is not installed correctly. Shut down and turn off your computer;
PPT007- The battery on your Mac needs to be replaced. The battery is in good condition, but its capacity has decreased significantly. Until you replace the battery, you can continue to use it without harming your computer.
VDC001, VDC003, VDC004, VDC005, VDC006, VDC007- A problem has probably been detected with the SD card reader;
VDH002, VDH004- There is probably a problem with the storage device;
VDH005- Cannot start macOS recovery;
VFD001, VFD002, VFD003, VFD004, VFD005, VFD007- There is probably a problem with the display;
VFD006- There is probably a problem with the GPU;
VFF001- There is probably a problem with the audio hardware component.
In any case, if you avoid repairs in service center failed, we strongly recommend that you contact only certified specialists who specialize exclusively in Apple technology. It won't be cheap, but buy new gadget much more expensive. It’s better to completely forget about the basement workshops “at Uncle Vasya’s”. Repairing Apple devices requires a very meticulous approach and advanced skills.
Today we’ll talk about collecting diagnostics in macOS
Information about the computer and programs
If you select “About This Mac” from the Apple menu and then click on the “System Report” button, you will see a bunch of all sorts of information about your computer. So, the system_profiler utility is the same thing, but a hundred times more detailed.
If you call system_profiler without parameters, the entire information will be displayed, which in my case means 3.8 MB of text. So I recommend immediately writing something like system_profiler > ~/Desktop/profile.txt or using grep to find the required line.
MAC diagnostics
Among what system_profiler spits out, you will find information not only about the system and devices, but also about all programs, drivers, plugins, libraries and fonts. At the same time, parts of the system logs and a bunch of other crap will be displayed.
If all this does not interest you, write system_profiler -detailLevel mini, and then you will only get information about the computer.
You can also add the -xml parameter to make it more convenient to process the received information in the script.
Directory service
The dscl - Directory Services Command Line utility is responsible for communicating with the directory service; it at one time replaced netinfo. Got a whiff of sysadmin stuff? This is true, and we will not dwell on them in detail.
For starters, a couple of commands: dscl . -list /Users will list all users, and dscl . -read /Users/<имя пользователя>- information about the user in XML form. Even a file with an avatar is encoded inside!
By the way, if you run dscl without parameters, it will enter interactive mode, where you can use the usual cd and ls commands for navigation, and view the contents of branches using the read command.
Directory Services caches and user list
Dscl comes with another utility, dscacheutil, which is responsible for working with directory service caches. You probably know it much better than dscl, because for a long time it was precisely this that needed to be run to reset the DNS cache.
By the way, in latest versions This does not work on macOS, and instead of dscacheutil -flushcache you now need to write killall -HUP mDNSResponder.
MAC diagnosticsAs for dscacheutil, it is convenient to use it to display a list of users: dscacheutil -q user. Unlike what dscl outputs, the result is much easier to perceive.
Reading and (not) resetting values in NVRAM
Every Mac has non-volatile memory that stores variables important to the computer's operation. What exactly is there? The nvram command will help you find out: write nvram -xp, and you will see everything.
There are both harmless things like sound level and the latest keyboard layout, as well as more interesting ones like the Find My Mac key and completely mysterious EFI parameters.
All of them are presented in binary form, and the only fragment of a description that I could find is contained in a CIA document leaked and posted on WikiLeaks.
Parameters can be set with the nvram command<переменная>=<значение>, delete with nvram -d command<переменная>or load from file using nvram -f<файл>.
You can reset everything by typing nvram -c. But usually NVRAM parameters are reset only if something went wrong and the computer does not boot. To do this, press Alt-Cmd-P-R immediately after turning it on and hold it for 20 seconds.
Please note: if you change parameters using the nvram utility, they will not be written to non-volatile memory instantly, but only when the computer is turned off in normal mode.
RAM statistics
There are many ways to see how much RAM is used. Perhaps the simplest is to open the “Memory” section in “System Monitoring”: the most useful parameters are presented there in a visual form. From command line It's best to use top.
If you need the most detailed information, then you can refer to vm_stat. The disadvantage of this utility is that all values are given in pages equal to 4 KB. However, it is not so difficult to recalculate, and there are a lot of scripts on the Internet - for example, this one-liner in Perl converts everything into megabytes.
You can also use vm_stat to track changes in memory load over time. To do this, enter vm_stat -c<число> <секунды>, where the first parameter is the number of measurements, and the second is the interval between them.
Resetting disk cache in memory
The purge command helps you temporarily get a couple of extra gigabytes of RAM. It is called from root, has no parameters and clears the disk cache, bringing it to the state it was in after loading the OS. But usually the memory manager does not need such help - it will gradually unload the excess if the RAM runs out.
The certificate says that purge is generally needed mainly for testing, but who knows how life will turn out?
File system access tracking
The fs_usage command, launched without parameters as root, displays a record of each access to the file system. This is needed in cases where a program crashes on startup or produces mysterious error messages. If the problem is that one of the files is damaged, then you can find it with fs_usage.
To reduce the need to rummage through the results, limit the messages to one process by writing its name after fs_usage. If you only know the ID, type sudo fs_usage pid .
Another useful parameter is -f, after which you can set a filter for operations with the network (-f network), with files (-f pathname will add a column with the path) and so on. If the text does not fit on the line, add -w.
The easiest way to avoid the help of service centers when searching for hardware problems (not all of them can boast of a good reputation) is to use the built-in Mac diagnostic methods. In this material we will tell you how to run and use the “Apple Hardware Functional Test” and “Apple Diagnostics”.
Using standard diagnostic tools, you can effectively detect hardware faults (problems with the hard drive, solid-state drive, RAM, graphics processor, motherboard and other nooks and crannies of the hardware). How to do this?
On which Macs which utility?
Regardless of the Mac model (MacBook, iMac, Mac mini or Mac Pro) and year of manufacture, the operating system includes a utility for self-diagnosis of the hardware. On computers manufactured before June 2013, it is called the Apple Hardware Test (AHT), and after that it is called Apple Diagnostics.
Before starting any of the utilities, be sure to disconnect all peripheral devices (including optical drives, if you still have such an antiquity) except the keyboard, mouse, display and Ethernet adapter. Some versions of OS X Lion and later may require Ethernet or Wi-Fi to run the Internet version of AHT. It is no different from its offline counterpart.
To use AHT, be sure to connect your MacBook to a power source.
List of keyboard shortcuts
If you don’t have a mouse, the following shortcuts will come in handy:
- Option (⌥) + D: run diagnostics with the Internet;
- Command (⌘) + G: start operation;
- Command (⌘) + L: display a list of languages;
- Command (⌘) + R: run the test again;
How do I use Apple Hardware Test or Apple Diagnostics?
Note: Apple Hardware Functional Test and Apple Diagnostics work identically. The only caveat is that Apple Diagnostics requires an active Internet connection to run, and the interface will be much prettier.
1. Turn on or restart your Mac if it is turned on.
2. While powering on, press and hold the "D" key until the gray boot screen appears, then wait a few minutes for the AHT configuration to complete. During loading the following icon will be displayed:
3. Now select the language and press the button to the right (if a mouse is not connected to the computer, then select the language using the arrows and enter with the “Enter” key).
4. After the ANT console boots up, select one of the tests you want to run.
Main test— press the “Test” button, or the T or “Enter” key.
Full test— under the “Test” button, check the “Run advanced test” checkbox.
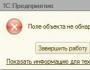
After the check is completed, the results will be displayed in a window located in the lower right corner of the console.

To exit the ANT utility, click the “Restart” or “Turn Off” button at the bottom of the window.
What do the results say?
If problems with the hardware are detected during the test, then get ready to see an error and some explanatory details.
You can decipher AHT errors on the Apple technical forum, and in general I recommend that you go there first when looking for solutions to problems with Apple gadgets. True, you will need knowledge of English, at least with a dictionary.
Apple Diagnostics error codes and their interpretation can be viewed.
In any case, if it was not possible to avoid repairs at the service center, we strongly recommend that you contact only certified specialists who specialize exclusively in Apple equipment. It won’t be cheap, but purchasing a new gadget is much more expensive. It’s better to completely forget about the basement workshops “at Uncle Vasya’s”. Repairing Apple devices requires a very meticulous approach and advanced skills.
Based on materials from yablyk
Any device, regardless of its complexity, requires a preventive inspection from time to time in order to promptly track emerging problems, eliminate them in time at their inception stage and prevent reappearance. Despite the fact that Macs (both desktop and mobile) are famous for their reliability, they should also undergo preventative maintenance from time to time. Mac OS X contains many different settings and temporary elements, both at the software and hardware levels, that can affect the operation of the system as a whole and individual applications. We will talk about this in today's article.
We would like to warn you right away that not all of the tips below should be used in any case - some of them are recommended to be used only in case of obvious problems.
IRON PREVENTION
Maintenance of hardware by the user consists of working with PRAM and PMU settings, data from the boot volume of the disk and the partition table structure. If you have the proper user skill and experience in assembling and disassembling your Mac, you should regularly clean its insides from dust.
- Checking the primary disk partition
We reboot the computer, but boot not as usual, but from a recovery disk or from any other boot volume (installation DVD, backup copy of the main partition, etc.). During the boot process (when using the installation DVD) or after a complete boot, run Disk Utility and, having selected the main partition with the system in it, we perform a disk check to find out if everything is in order with the structure of the disk file system. The same check can be done by booting into normal mode, but if loaded from another medium, the verification efficiency will be slightly higher.

- Apple Hardware Test
For any Mac, there is also an official tool for testing hardware for errors. It's called Apple Hardware Test and can be found in a variety of places:
- on installation disk with Mac OS X that came with your Mac (if you bought it with Leopard 10.5.4 or older)
- on the software disk that came with the Mac (if Mac OS X 10.5.5-10.6.8 was pre-installed on the Mac)
- on the Recovery partition or even on the Internet (if the Mac was sold with OS X Lion)
Depending on the Mac models, the way you run the test may vary. As a rule, to enter the test you need to hold down the D key when turning it on (not when rebooting!). If Apple Hardware Test is located on the Recovery partition of the disk, then use the Command+D combination.
If the D key doesn't change anything, try inserting the disks your Mac came with into the drive and holding it down when the computer turns on with a DVD in the drive.
If Apple Hardware Test finds any errors, it will be very important to remember (or better yet, write down) their codes. This will be useful to you when communicating with technical support.
If there is no other medium from which to boot, there is no need to bother with Disk utility I don’t want to either, then you can boot your Mac into safe mode. This mode is good because, among other things, with this start, several system maintenance procedures will be launched and the disk will be forced to check for errors. In order to boot the original Mac in safe mode, the user just needs to hold down the key while booting. SHIFT , in case of using Hackintosh - boot with the flag -x .
- Resetting PRAM
PRAM is a parametric random access memory device that stores some operating system and device settings to provide Mac OS X with quick access to them. The number and name of settings varies depending on the type of computer, as well as the devices and drives connected to it. But almost always, video and monitor settings are stored there (refresh rate and screen resolution, number of colors and some others), information about the starting disk volume, set speaker volume, data about the last kernel panic.
In some cases, clearing PRAM helps to cope with certain problems that have arisen. To clear PRAM, just hold down the keys when starting the computer COMMAND+OPTION+P+R (you need to press them before the gray screen appears) and do not release until the Mac boots up and you hear the Mac OS X welcome sound.
If you have a RAID array installed on your Mac, it may turn out that after resetting the PRAM, the computer will refuse to boot correctly. In this case, you should try to boot while holding down the key OPTION to the screen for selecting a system to launch, and if this does not help, then restart the Mac by holding down the keys COMMAND+OPTION+SHIFT+DELETE .
- Reset SMC
An SMC module is a computer chip that is usually found on the motherboard and is responsible for managing all aspects of the computer's power supply. It controls the speed of rotation hard drive, turning sleep mode on and off, charging, and the effect of connected devices on sleep mode. If you have problems with sleep mode, the inability to turn on the computer when running on battery power, and other power-related problems, then resetting the SMC settings can help solve them. For different Macs, the SMC reset process is slightly different, so to get reset instructions specifically for your Mac, we refer you to the Apple knowledge base, where everything is described in detail. As an example, we give the procedure for resetting the SMC for MacBook Air And Mac Mini.

- Turn off your MacBook and disconnect all cables from it.
- Connect the network adapter cable to it.
- Press and hold the keys CONTROL+SHIFT+OPTION on the left side of the keyboard (that's right), and then press and hold the power button.
- After 5 seconds, release all buttons and press the power button again.

- Disconnect all cables from the computer, including the power cord.
- Wait 10 seconds.
- Plug in the power cord while holding down the power button on the back of the computer.
- Release the Power button.
- Turn on your computer by pressing the power button again.
- Cleaning your Mac from dust
This procedure requires some experience and practice in disassembling and reassembling a Mac. Despite its apparent complexity, the operation can significantly help in the fight against insufficient cooling of the computer case and components, because the Mac, like any other electronic equipment, is an excellent dust collector. Of course, not every Mac can be easily disassembled. You can find out how this is done and how difficult it is on the iFixit portal.

However, if you are not confident enough in your abilities, then it is better to clean your Mac from dust at a service center.
PREVENTION OF THE SYSTEM
System prevention comes down to checking the status of rights to files and folders, clearing various caches and removing other garbage.
- Verification and restoration of rights
It may be quite useful to check and, if necessary, restore access rights to files and folders. To do this, boot in normal mode from the main boot partition and start again Disk Utility, in which we perform the above operations.

- Extraordinary launch of the Mac OS X self-cleaning system
Mac OS X is enough smart system and it has a built-in self-cleaning system that independently removes various temporary files and other garbage. Everything would be fine, but there is one problem - the self-cleaning system starts at strictly defined hours, when the computers of Russian users, as luck would have it, are turned off. About how to solve this problem and independently start the self-cleaning process in detail in one of our articles devoted to working with the Terminal.
- Cleaning extensions and system cache in Mac OS X
At possible problems cleaning system extensions can help with drivers, and cleaning system cache will help the system “breathe” more freely. For detailed description cleaning process also refer you to the above-mentioned article on working with the Terminal.
The final finishing touch to prevent the operating system is to restart the computer. Don't be surprised if your Mac takes too long to boot the first time after cleaning - this is normal. Reboot the machine again and it will boot normally.
Alternatively, to prevent the system, you can use various specialized applications that significantly facilitate this process and eliminating operations with Terminal, Disk Utility and other applications that frighten newcomers. We have already talked more than once on the pages of our website about similar programs, for example, or.
Keep your Mac in order, take care of it regularly and it will repay you with many years of impeccable work;)
As you know, Apple pays a lot of attention to organizing the maintenance and repair of its devices... while they are under warranty. If your MacBook is out of warranty, repairing it can cost a significant amount of money. You may be charged several hundred dollars for some minor problem.
Therefore, let's look at those problems that we can fix ourselves. Here I have collected all important information DIY MacBook repair. It will also be useful to users desktop computers Mac.
Before you begin: Backup
If your MacBook has started to have problems and you are planning to deal with them, then before you proceed, create backup copy all important information.
Hopefully you already know how to use Time Machine. Use this utility to create a copy of your Mac on external storage or online storage. Great, let's start troubleshooting the MacBook and fixing it.
1. Download updates and check for viruses
In the first step, make sure that you have installed current versions software. Download the latest updates for your operating system, applications, component firmware... absolutely everything. Run App Store and go to the “Updates” section. If an update is ready for a software product, install it. 
If you installed some programs not through the App Store, then run each of them separately and check if they are ready to update.
After updating your programs, run an anti-virus scan (after updating your anti-virus) to make sure there are no viruses or other malware that could be causing problems with your computer. You can also use a program to search for and remove adware, such as Adware Mdic. Just don't use MacKeeper for this.
Many users still live in the dark and believe that viruses do not threaten Macs. But the situation has long changed, and unwanted programs that display advertisements can easily get installed on your system.
After updating and checking for viruses, restart your computer. It is possible that it will work without problems.
2. MacBook diagnostics
If the problem persists on your Mac, you need to find out its source. First you need to decide on the category of the problem: software or hardware. To check your hardware, you need to run Apple Diagnostics (or Apple Hardware Test, depending on the age of your computer). To do this, we will use the following algorithm:
- Turn off your MacBook and disconnect all peripherals from it (except the network adapter, mouse, keyboard, and Ethernet connector).
- Hold down the D key until Apple Diagnostics starts loading.
- Select your language and press the Enter button.
- If your Mac was released before 2013, then select “Perform extended testing” and click “Test”.
 The procedure for diagnosing the computer hardware will begin. This may take a while - be patient. Once the diagnostics are complete, a table will appear on the screen with information about the hardware problems found. Write all this down somewhere and restart your computer.
The procedure for diagnosing the computer hardware will begin. This may take a while - be patient. Once the diagnostics are complete, a table will appear on the screen with information about the hardware problems found. Write all this down somewhere and restart your computer.
Using the built-in Disk Utility in OS X, you can detect a number of problems related to file system, especially if they are related to access rights.
If these diagnostic tools do not find anything, you will have to use alternative method. Learn “Localizing problems in Mac OS X” - in this document, Apple has collected useful tips to help you find the source of problems with your computer. Once you find it, you may be able to figure out your next strategy. MacBook repair or you will have to look for relevant information on thematic forums.
If you still don't know how to return full functionality your Mac, read the article further.
3. Problematic programs
Let's start with what is simpler. As a rule, problems with software are solved cheaper and faster.
Correcting access rights
Incorrect permissions often create problems that are difficult to explain. Fixing them in many cases allows you to quickly solve seemingly incredibly complex problems. Run Disk Utility(Applications -> Other) and click the “Check access rights” button.
 The utility will almost certainly find several objects whose access rights it will recommend correcting. After it completes its work, click the “Correct access rights” button. If the list of fixes is large enough, this procedure will take several minutes. You can relax and have a cup of coffee for now.
The utility will almost certainly find several objects whose access rights it will recommend correcting. After it completes its work, click the “Correct access rights” button. If the list of fixes is large enough, this procedure will take several minutes. You can relax and have a cup of coffee for now.
Resetting PRAM and SMC
System random access memory (PRAM) and system management controller (SMC) are responsible for many important things on your Mac. To reset PRAM do the following:
- Turn off your computer.
- Press the computer's power button.
- Before the gray screen appears, press the Command, Option, P, and R buttons simultaneously.
- Hold these buttons until you hear the computer boot sound again.
- Now release the buttons.
Resetting the SMC depends on the type of computer you are using. On a MacBook with a removable battery:
- Turn off your computer.
- Disable network adapter nutrition.
- Remove the battery.
- Press and hold the power button for five seconds.
- Reinsert the battery.
- Turn on your computer.
On a MacBook with a non-removable battery:
- Turn off your computer.
- Connect the AC power adapter.
- On the built-in keyboard, press the Shift, Control, and Option buttons on the left and the Power button at the same time.
- Release Shift, Control and Option at the same time.
- Turn on your computer.
On Mac Pro, iMac with Intel processor, Mac Mini with Intel or Xserve on Intel:
- Turn off your computer.
- Unplug the power cord.
- Wait fifteen seconds.
- Connect the power cord.
- Turn on your computer.
Removing problematic programs
If you still can't get your MacBook to work properly, and you suspect a particular program is causing problems, then try uninstalling it and see if your computer works better after that. If this is exactly what happened, try installing this program again. Sometimes that's all you need to do to repair your MacBook. If problems persist, then try a few more things.
Reinstalling OS X
We are moving to decisive measures. Sometimes in operating system A serious problem arises that can only be resolved by reinstalling. That's why you backed up your Mac at the beginning of this article.
If you have OS X Yosemite installed (you've already updated your Mac), proceed as follows:
- Restart your MacBook.
- When you see a gray screen, press and hold Command + R.
- Options should appear, from which select “Install OS X”.
- Follow the instructions on the screen.
- The operating system will be reinstalled. See if the problem goes away.

4. Hardware problems
If your MacBook has a hardware problem and you want to fix it yourself, you will have to use online resources filled with useful information. Apple Information Diagnostics or Apple Hardware Test should be the starting point (of course, if this utility has started and the computer display is working). Sometimes diagnosing problems in hardware can be very difficult and will require professional skills and tools.
Collecting information
Before you begin repairing your MacBook hardware, you should be well prepared and collect the necessary information. There are quite a lot of resources on the Internet about repairing Macs. I recommend starting with iFixIt, Instructables and YouTube. Before disassembling the MacBook case, carefully read or watch the instructions and make sure you have everything you need.
MacBook Repair Tools
Unfortunately, to repair Apple laptops you will need tools that are not included in the traditional home kit. In the iFixIt online store and at local hardware markets you can find almost everything you need: clever screwdrivers, soldering tools and special kits. 
You can also search Amazon and eBay for the repair tools you need. In the latter case, the prices may pleasantly surprise you (but delivery will most likely cost a pretty penny). Used tools are unlikely to lose their functionality after repairing one or two computers.
Where to get spare parts
On eBay you can find not only tools, but also spare parts for MacBook: from motherboards to displays. You can also buy a faulty Mac inexpensively, in which we will find many working parts for repair. iFixIt also sells Mac parts.
Before buying, check a hundred times that this is exactly the part you need. Protect yourself from incompatibility problems. If you are not sure what exactly this part is called, on your MacBook go to the Apple Menu (in the upper left corner of the screen) -> About This Mac -> System Report and find a description of the required component there (of course, if the computer turns on) .
Get to work!
If you know what needs to be done, have prepared the tools and the necessary spare parts, then it’s time to start repairing your MacBook. Re-read the necessary instructions. Protect yourself from possible electric shock and proceed.
Be patient. Repair modern computer- a very delicate task, there are many small and fragile parts, and some of them can irreversibly damage the discharge static electricity. Be extremely careful when working with batteries and microcircuits.
Or maybe to a service center?
Fixing a MacBook takes time, patience, and sometimes a lot of money - but it results in the return of the computer's functionality and increased self-esteem.
I recommend undertaking serious repairs only if you like to delve into the inside of electronic devices. Having solved serious hardware problems with Macs several times, you will move to a select group. 
But for most of us, serious Mac repairs should be left to a properly trained professional. You can try to take the relevant courses yourself. But they are unlikely to seem simple to you. Therefore, most users entrust the repair of their MacBook to professionals. Yes, you will pay more money, but you will receive qualified help.
In what situation are you ready to repair your computer yourself? And when would you prefer to entrust its repair to a qualified person? Share your opinion in the comments.